Your Guide to Hypertension
One in three American adults have high blood pressure. That’s roughly 65 million people—plus many more are at risk. Over half of all Americans 60 years of age and older have it.
What is hypertension?
Your arteries and blood vessels send blood from your heart throughout your body. When you have high blood pressure, also known as hypertension, the force of blood pushing against your blood vessels is too high. This causes them to narrow. In turn, this makes it harder for blood to get where it needs to go.
What are the risks?
What makes high blood pressure so dangerous is it increases the risk of many other serious conditions, like stroke, heart attack and kidney disease. And it often doesn’t show symptoms. Studies show that roughly 35% of adults are unaware they have high blood pressure. In some cases, you may experience symptoms like headaches, chest pains, shortness of breath and dizziness. It can be easy to write off these symptoms as something else.
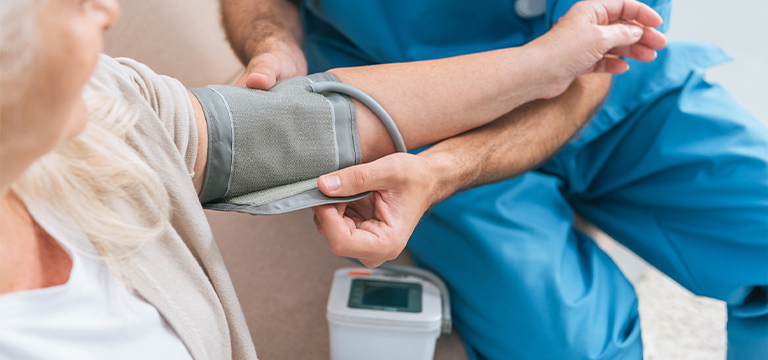
This is why regularly visiting your primary care provider to get blood pressure readings is so important. Usually, this is done during your annual physical. However, depending on your personal health, your doctor may recommend more frequent readings.
Can it be treated?
The good news is there are a lot of different treatment options. Treatment ranges from lifestyle changes to medication—or both. If you’re diagnosed with hypertension, it’s important to work with your doctor to find the right treatment plan. Lifestyle changes are a crucial part to managing high blood pressure.
Be sure to eat a healthy diet. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is an eating plan designed specifically for reducing hypertension. It includes plenty of fruits and vegetables and low-fat/nonfat dairy. Avoid salt, saturated fats and trans fats. Studies have shown the DASH diet can lower blood pressure in as quickly as two weeks.
Get enough exercise. Cardio exercise helps you keep your heart and blood vessels circulating blood properly. Staying active outside of workouts is also important, like taking the stairs instead of the elevator or walking places instead of driving.
Aim to maintain a healthy weight. Losing as little as a few pounds can make a difference in your blood pressure. It’s also important to take your hypertension medication exactly as prescribed. It’ll help your doctor understand how it affects your blood pressure and if it’s working well.
Taking at-home readings can help you stay motivated to lower your blood pressure and track your progress. FEP members can get a blood pressure monitor at no out-of-pocket cost through our Hypertension Management Program.* Click here to see how you can get yours.
*You must be the contract holder or spouse, age 18 or older, to receive this benefit.
Sources:
https://www.webmd.com/hypertension-high-blood-pressure/guide/high-blood-pressure
https://www.heart.org/en/affiliates/lowering-high-blood-pressure-in-the-puget-sound


